Occurrence:
I have solved a seepage analysis with the Land-Climate Interaction boundary condition. I would like to know how to calculate the water balance for my simulation.
Resolution:
Surface Water Balance
When conducting a seepage analysis with the Land-Climate Interaction boundary condition, you can calculate the surface water balance using the results collected from the Water Mass Balance graph category. The water balance at the ground surface can be calculated as follows:
P + M + E + R = I
Where P is the cumulative precipitation, M is the cumulative snowmelt, E is the cumulative evaporation, R is the cumulative runoff, and I is the cumulative net infiltration. The error associated with the water balance can be obtained by moving all of the terms over to the left-hand side of the equation. All of these variables are readily accessible in the Draw Graph window, and more specifically, in the Water Mass Balance category.
Further information pertaining to the surface water balance can be found in the following example
Domain Water Balance
The water balance of a SEEP/W analysis can also be calculated for the entire domain by comparing the cumulative mass of water that flowed past the domain boundaries to the cumulative change in stored mass (or cumulative change in domain water mass due to changes in storage and root water uptake), such that:
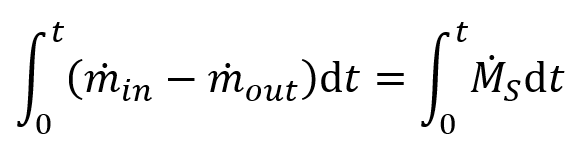
The terms that appear in this equation are readily accessible in the Draw Graph window, and more specifically in the Water Flow and Water Mass Balance graph categories, respectively. The apparent mass balance error can be computed as the difference between the cumulative change in stored mass computed at the subdomain and nodal levels, which is mathematically expressed as follows:
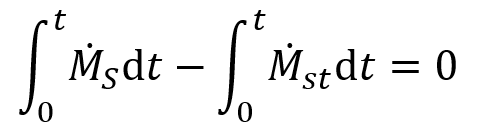
The relative apparent mass balance error is calculated by dividing the error by the maximum of the cumulative change in stored mass computed at the subdomain and nodal levels. The error is ‘apparent’ because it is a mathematical by-product of non-convergence, not an actual loss of mass, since the solution conserves mass. The error and relative error are reported in the Draw Graph window, and more specifically, in the Water Mass Balance category.
Further information pertaining to the domain water balance can be found in the following example.